1. 전기쌍극자(electric dipole) : 서로 다른 극성을 갖는 두 개의 전하가 작은 거리 d 만큼 떨어져 존재하는 것.
-> 전기 쌍극자로 인해 내가 받는 힘의 크기는 얼마?
-> 각 힘을 더하기
-> 값이 '0'이 아니다! (서로 다른 극성일 띤 거의 붙어있는 전하들로 인한 매이 멀리 떨어져 있는 곳에서의 electric field indensity는, 멀리서 볼 땐 거의 '0'로 보이지만 사실 field는 존재한다. Ex) 수소, 물 분자
Electric dipole monent p = ql (새로운 parameter)
2. A Summary of Gauss's l=Law
(1) If continuous distrubution of charge characterized by ρ(charge density) enclosed by s :
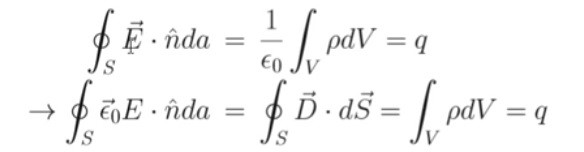
(*첫줄 q->q/ε)
This the INTEGRAL FORM OF THE GAUSS'S LAW in free space.
-> Total charge (q) enclosed by a closed surface (S) is equal to the surface integral of eletric flux density produced by the charge.
(2) If we apply the divergence/Gauss theorem to Eq.[A] :
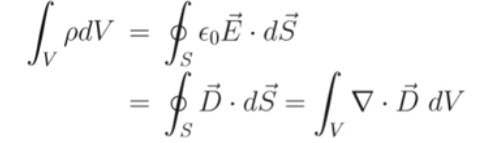
임의의 벡터를 벡터를 둘러싼 폐곡면에 대해서 적분한 값은, 그 벡터를 발생시킨 전하량과 같다.
(3) Since this is valid for any arbitray volume (V) with a closed surface (S), the equation of the integrand is to be valid, too :
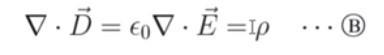
This the DIFFERENTIAL FORM OF THE GAUSS'S LAW in free space with a permittivity/dielectric constant ε.
(4) Gauss's Law directly shows us the CHARGE CONSERVATION within a closed surface. Furthermore, since a charge q in an energy source, this Gauss's law implicates A KIND OF ENERGY CONSERVATION
(5) D = ε0E , where ε0 = is the dielectric constant (or permittivity). Then the Gauss's law becomes
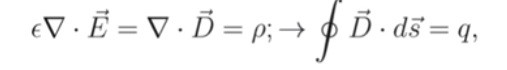
(6) AN ELECTRIC DIPOLE MOMENT (p) is defined as two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance : p = ql
-> 안테나, 레디에이션, 재료의 전기적인 성질 등을 계산할 때 매우 중요하다.
쿨롱의 F로 부터 계산할 수 도 있지만, potential(각각의 전하가 해 줄수 있는 일)로 부터 계산할 수도 있다!
'전공기초 > 전자기학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter 4-1 Gauss's Law (0) | 2021.11.10 |
|---|---|
| Chapter 3-2 Coulomb's Law (0) | 2021.11.10 |
| Chapter 3-1 Charge (0) | 2021.11.10 |
| 0. 전자기학의 역사 [맥스웰과 아인슈타인] (1) 전자기학의 시작 (0) | 2020.12.28 |